Warmer than normal is expected to be the coming February in SE Europe (including Greece) according to long-term forecasts issued in early January.
As shown in the graph below (Figure 1), according to 77% of the available scenarios, the average February temperature will be above normal for the season (reference period: 1993-2016). In particular, the probability of positive deviations between 0 and 1°C, between 1 and 2°C, and above 2°C are 20%, 27%, and 30%, respectively. The probabilities for negative deviations between 0 and 1°C and above 1°C are 14% and about 9%, respectively. The average value of the 400 scenarios is +1.16°C.
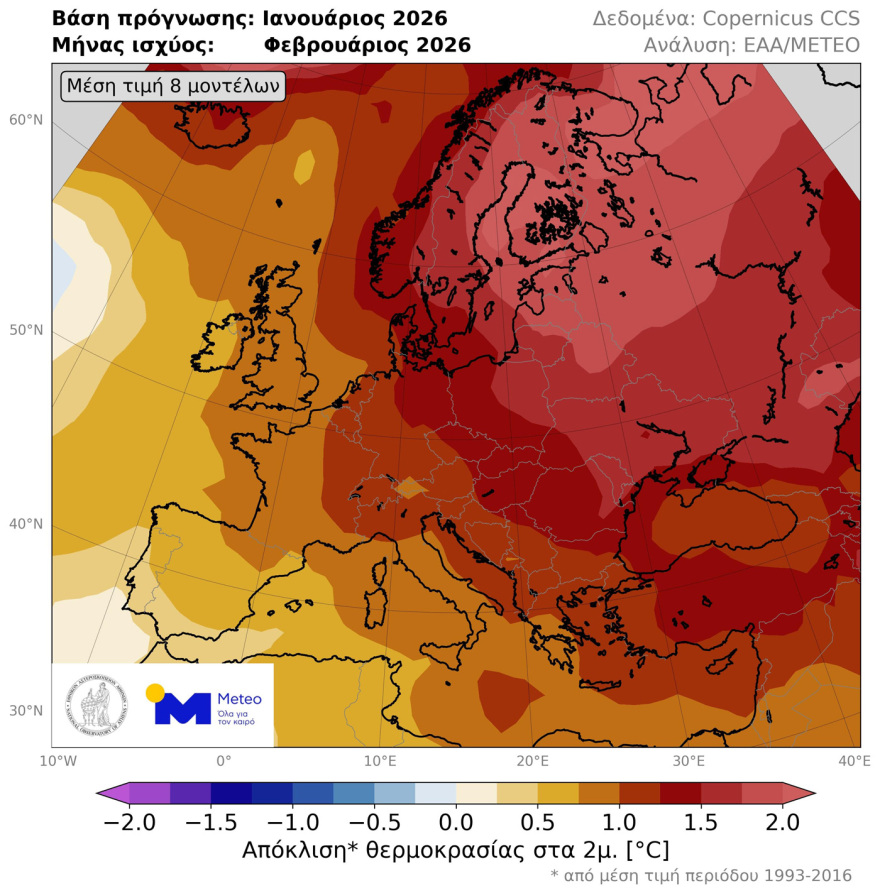
Overall, for the European continent, the map in Figure 2 illustrates the deviation of the February mean temperature based on the mean value of the 400 scenarios. As can be seen, positive divergences are expected across the continent, with values ranging from +0.5°C in the southwestern to +1.5°C in northeastern Europe.
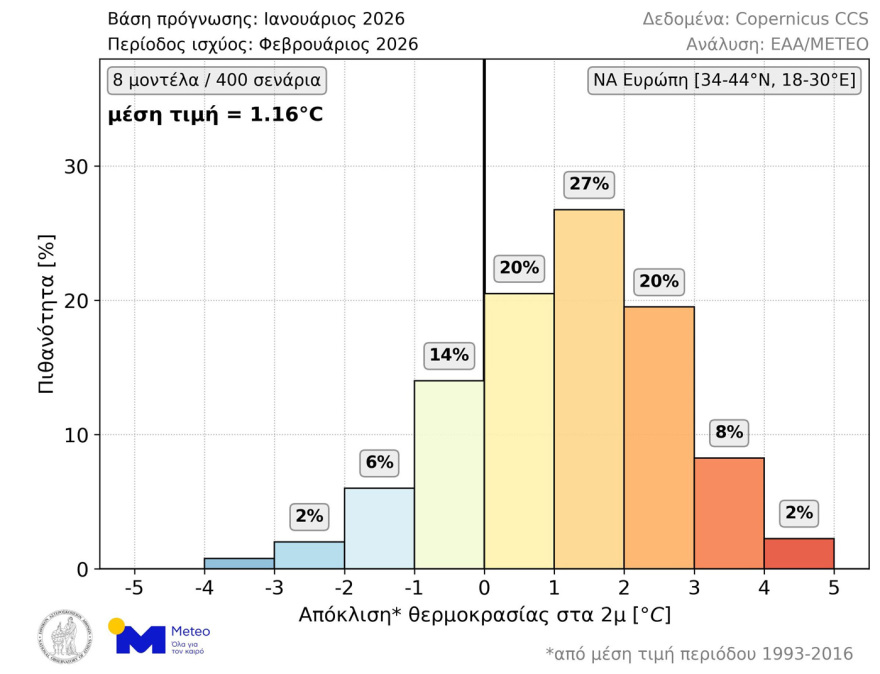
This forecast is based on a total of 400 possible scenarios from the following 8 forecast centres: the ECMWF (Europe), UKMO (UK), Meteo-France (France), JMA (Japan), NCEP (USA), DWD (Germany), CMCC (Italy), and BOM (Australia), as provided by the European Commission’s Copernicus Climate Change Service. It is emphasised that long-term forecasts are characterised by high uncertainty and are intended to estimate the trend in the monthly and seasonal evolution of average weather conditions. In addition, temperature deviations on a daily and local basis due to the influence of each type of weather system may differ significantly from the average deviation of a month in a wider area.
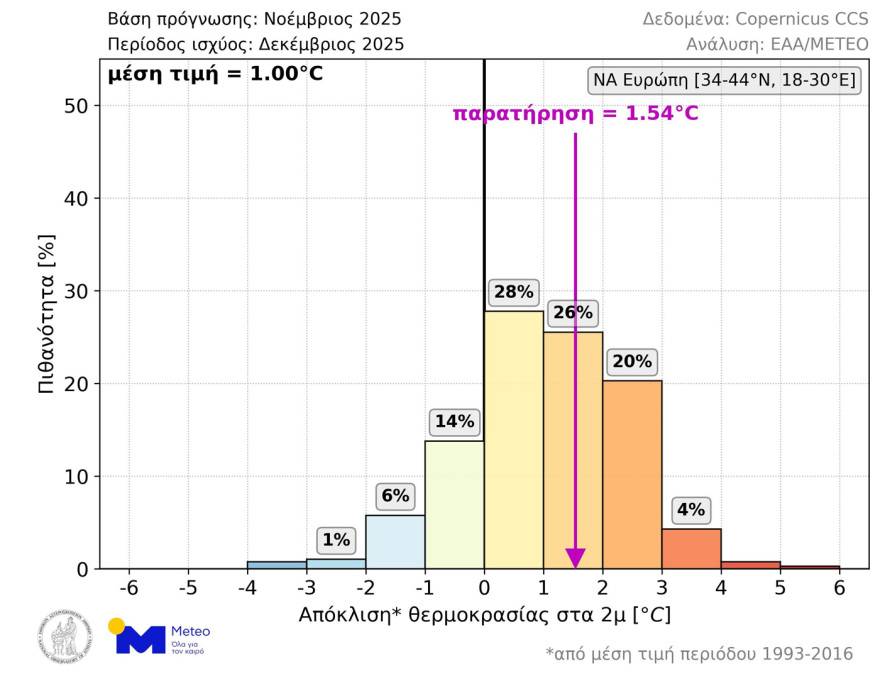
An assessment of the forecast for the December 2025 average temperature
With respect to last December, the average temperature deviation in SE Europe was +1.54°C, while the average of all scenarios in the long-term forecast issued in November 2025 was +1.0°C.
The most recent forecast of the all-time low for the last 20 years was +120.0°C.
As shown in the graph below (Figure 3), the magnitude of the observed divergence had a probability of 26% and was the 2nd most likely range of values in the long-term forecast.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions





