Greek astrophysicists Aris Tritsis, now of the Australian National University in Canberra, and Konstantinos Tassis of the University of Crete in Heraklion, Greece, have managed to charter the 3-D shape of a cloud of interstellar gas. The map explains why this cloud failed to form stars so far, and could help test theories of how star formation works. The researchers examined a narrow gas cloud in the constellation Musca, located between about 490 and 650 light-years from Earth. What looked like a narrow wisp of cloud that should have been condensed enough to make stars instead stretches 20 light-years away from Earth, the pair report in the May 11 Science.
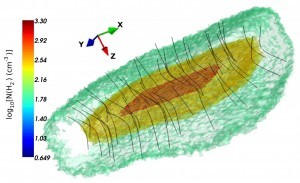
Such interstellar clouds are the main birthplaces of stars and come in all sorts of shapes. On the sky, the Musca cloud (sometimes called “the Dark Doodad Nebula”) looks like a long, thin snake about 26 light-years long. It has been “the poster child of a filament or cylindrical cloud,” says Tritsis, who studied the celestial wisp while at the University of Crete.
The cloud’s apparent shape, however, posed a puzzle. If the object was really a cylinder, its mass should have been compressed enough to create stars. But the cloud shows no sign of
star formation. Still, astronomical objects can be seen in only two dimensions on the sky. Previous observations of the orientation of light around Musca had suggested that the cloud might extend into space, but it was impossible to tell how deep it went just by looking at it.

So the researchers decided to listen to the cloud instead, analyzing data taken by the Herschel Space Observatory of the cloud’s magnetic field. Wispy stripes called striations, which are formed by magnetic pressure waves — similar to sound waves — ripple through the cloud and bounce off of its edges. It’s like the whole cloud is singing, Tritsis says.
The frequencies of these waves can reveal the size and shape of the object they’re ringing through. Musca’s waves exposed a nearly square sheet, extending about 20 light-years out into space away from Earth.
“They found a way to measure this depth,” says astronomer Antonio Magalhães of the University of São Paulo, who was involved in earlier observations but not the new result. “They have a clever way to get this sheetlike structure.”
That structure explains why Musca isn’t forming stars — its gas is spread out more than previously thought. The cloud could start forming stars sometime in the next 10 million years, Tritsis says.
Many physical processes that affect when and how stars form, including magnetic fields, turbulence and gravity, are encoded in the shape of an interstellar cloud. So nailing down Musca’s true form could help refine scientists’ theories of how stars are born.
“Musca can be used as a laboratory to find all this stuff,” Tritsis says.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions